Publications and Others
Click a title to view the abstract.
-
Single-sex schools and students’ Physical Health: Evidence from National Physical Test in South Korea (with Youngjoo Jung, Economics Letters, 2025)
Abstract: Leveraging a randomized natural experiment, this study examines the impact of attending single-sex middle schools on students' physical fitness, measured through standardized nationwide physical tests. In South Korea, middle school students are assigned by lottery to either single-sex or coeducational schools within their designated school zones, providing an ideal setting to evaluate the effects of single-sex schooling. Using school-level data covering all middle schools, the study finds that boys attending single-sex schools achieve significantly higher pass rates on standardized physical fitness tests, suggesting improved physical fitness compared to their peers in coeducational schools. However, no similar improvement is observed for girls attending single-sex schools. These findings suggest that single-sex schooling has differential effects by gender, highlighting the need to further research to understand the mechanisms underlying these varied outcomes. 📄 View Paper
-
Analysis of Unemployment Insurance Claimant Experience Survey (with Eliza Forsythe, Report prepared for the Illinois Department of Employment Security (IDES))
Abstract: This report analyzes the Illinois Unemployment Insurance (UI) Claimant Experience Survey, conducted between August 2023 and August 2024, with the goal of improving equity in access to UI benefits and strengthening survey design. Using regression analysis of demographic characteristics and text analysis of open-ended responses, we examine how claimants’ backgrounds and filing circumstances shape their reported experiences with the UI system. The study focuses on key dimensions of the claimant journey, including sources of information, reliance on in-person services, perceived difficulty of filing, and narrative accounts of the process. By combining quantitative and qualitative evidence, the report provides insights into heterogeneity across demographic groups and filing types, and develops recommendations for improving data collection, reweighting procedures, and survey integration to support more representative and actionable insights for IDES.
Working Papers
Click a title to view the abstract.
-
Disrupted Support, Disrupted Careers: Time Constraints and Skilled Women's Labor Market Response (Job Market Paper)
Abstract: Skilled women often rely on outsourced household services to maintain demanding careers. This paper examines how disruptions to these services affect skilled women’s labor supply across occupations with different returns to working longer hours. I develop a time-allocation model formalizing the mechanism and test its predictions using the staggered rollout of Secure Communities—an immigration enforcement program that targeted low-skilled immigrants, who constitute a large share of the domestic-service workforce. I show that the policy contracted the household-service market by reducing supply and increasing wages of domestic workers. Consistent with the model, women in occupations with higher returns to working longer hours reduce working hours and reallocate time to household production following the contraction, reflecting their greater reliance on external household services before the shock. Among married women, reductions are smaller when spouses hold flexible jobs. These findings show that tighter time constraints make high-return occupations harder to sustain for women, widening gender gaps within occupations and contributing to broader disparities. The results highlight the importance of household-service capacity and family support for women's advancement in such careers.
-
Impact of the Drug Crisis During Adolescence on Educational and Labor Market Outcomes (with Sunny Liu)
Abstract: Drug overdose in the United States has increased over six times in the past three decades. We investigate the education and labor market consequences of adolescent exposure to the drug crisis. Previous research has largely focused on the direct labor market effects on drug users. Our paper shifts focus to the long-term consequences, specifically examining the educational attainment and labor market outcomes of adolescents who grew up in communities affected by the drug crisis. To mitigate potential omitted variable bias, we instrument for the severity of teens' exposure to the drug crisis using the state-level triplicate prescription programs, which influenced pharmaceutical companies' marketing strategies. By leveraging the variation in these state-level policies, we establish a causal link between the drug crisis and teenagers' outcomes in adulthood. We further shed light on the potential mechanisms by looking at direct effects on individuals and indirect effects on neighborhood amenities. Given the potential lifelong consequences of education and early career experiences, this research offers vital insights into the broader societal consequences of the ongoing drug crisis.
-
Unintended Benefits: Immigrant-Inclusive Policy, Mental Health, and Risk Behaviors of Hispanic Adolescents
Abstract: Research shows that restrictive immigration enforcement adversely affects Hispanic communities, yet the effects of immigrant-inclusive policies remain largely unstudied. This paper examines whether state-level sanctuary policies affect mental health and risk behaviors among Hispanic adolescents. Using a difference-in-differences design, the analysis finds substantial mental-health improvements: sadness declines by 10 percent and suicidal ideation by 16 percent. Risk behaviors also fall, with smoking initiation decreasing 35 percent, current smoking 15 percent, and alcohol consumption 9 percent. These findings reveal spillovers beyond the policies’ initial goals, benefiting the broader Hispanic population. Given the links between adolescent mental health and later labor-market outcomes, and the substantial economic costs of risky health behaviors, these results indicate that immigrant-inclusive policies generate broad benefits that should be incorporated into immigration-policy evaluation and design.
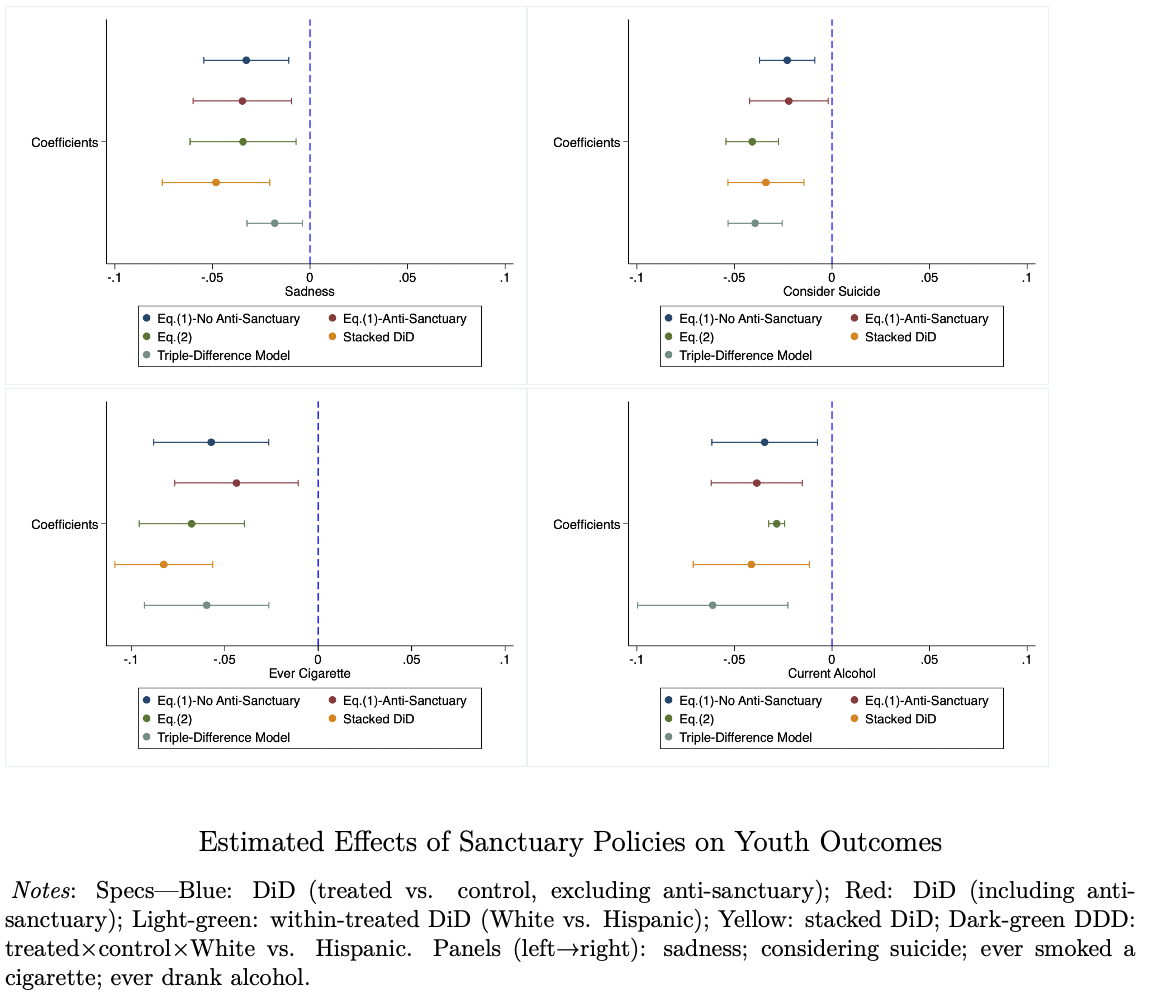
Figure: Effects of sanctuary policies on adolescent mental health and risk behaviors. -
Effects of Eliminating Early Morning School Hours on Adolescents’ Sleep Patterns, Health, and Time Use
Abstract: By examining the nine o'clock attendance policy implemented in Gyeonggi Province of Korea, this paper investigates the effects of eliminating early morning school hours on adolescents’ sleep patterns and health. The analysis shows that the policy significantly delayed adolescents' wake-up times on weekdays. However, this increase in sleep duration was partly offset by postponed bedtimes. Additionally, the sleep gain has decreased over time. On weekends, wake-up times show no statistically significant change while bedtimes shift later, leading to decreased weekend sleep duration. The paper also shows that the policy adversely affected adolescents' health. To identify the possible mechanism, this paper also examines its impact on their time use. The results indicate that adolescents spent more time studying, possibly due to the school imposing additional academic work in response to the later start time. The changes in their time allocation, accompanied by the delayed bedtimes, may have affected their health via the policy.
Work in Progress
- Cure Model Difference-in-Differences Estimator (with Wonjun Choi and Juhyeon Oh)
- Opioid Crisis and Firm Response
- Racial Segregation and Health: Evidence from Historical Railroad Configuration
